
The process of binary fission occurs under favourable conditions, or the cell divides under the favourable conditions that include temperature, surroundings and the availability of nutrients.Ĭertain organisms that divide through binary fission include Euglena, Amoeba, Paramecium, Ceratium, Clostridium perfringens, Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, B. When the cytokinesis follows the oblique pattern of division, it is known as oblique binary fission, and this is seen in Ceratium (dinoflagellates). When the cytokinesis occurs along any plane or axis and is always perpendicular to the plane of the division of the nucleus of the cell is known as irregular binary fission, it is commonly observed in amoeba. In the longitudinal binary fission, the cytokinesis is held along the longitudinal axis of the cell and is usually seen in Euglena.
/GettyImages-103311355-490ad3ba66d44d40b738a0e7d468ac8a.jpg)
This type is generally seen in Paramecium (ciliated protozoans). When the division of cytoplasm (cytokinesis) occurs along the transverses axis is known as transverse binary fission. There are four different types of binary fission observed in the unicellular organisms that are – Transverse, longitudinal, irregular and oblique. In this way, the daughter cell receives the one copy of the genetic material of their parent cell.īinary fission is the stable process, and genomes of the unicellular organism do not undergo mutations. Gradually, the cytoplasm also separates with the separation of the two nuclei and thus forming the two new daughter cell. So, the nucleus which contains the genetic material replicates itself, by pulling the two nuclei to opposite poles. In the process of binary fission, the parent cell prepared itself by making a copy of their genetic material (Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA) before getting divided. It is the primary method of reproduction in prokaryotes. The process of asexual reproduction, where the parent body gets separated or divides into two new bodies or cell, is known as binary fission. Numerous daughter cell, so multiple nuclei are formed from the parent cell.Įuglena, Amoeba, Protozoans, Bacteria, flatworms, etc. Two daughter cells' so two nuclei are formed from the parent cell. Cyst or protective covering is formed during division.ĭuring favourable as well as unfavourable conditions.
The nucleus divides, which gets surrounded by cytoplasm.ģ. Nucleus, as well as cytoplasm, divides simultaneously.ġ. When the parent cell divides and gives rise to numerous daughter cells.ġ. When the parent cell divides into two equal parts and gives rise to the two daughter cell is known as binary fission. We will also be discussing the process of reproduction. However, in this context, we will be studying the two terms related to asexual reproduction and how they differ with each other, which are binary fission and multiple fission. There are various types of asexual reproduction which have been observed till now, such as – fission, budding, fragmentation, spore formation, vegetative propagation and parthenogenesis. Sexual reproduction is the process where there is the involvement of two-parent cell (fusion of gametes), which reproduce and give birth to the new individual In contrast, asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell, that divides its nucleus and gives birth to their offspring.Īsexual reproduction occurs in unicellular organisms like bacteria and archaea and at multicellularity level in plants, fungi and few lower animals. We all are aware of the fact that reproduction is also of two types – asexual and sexual.
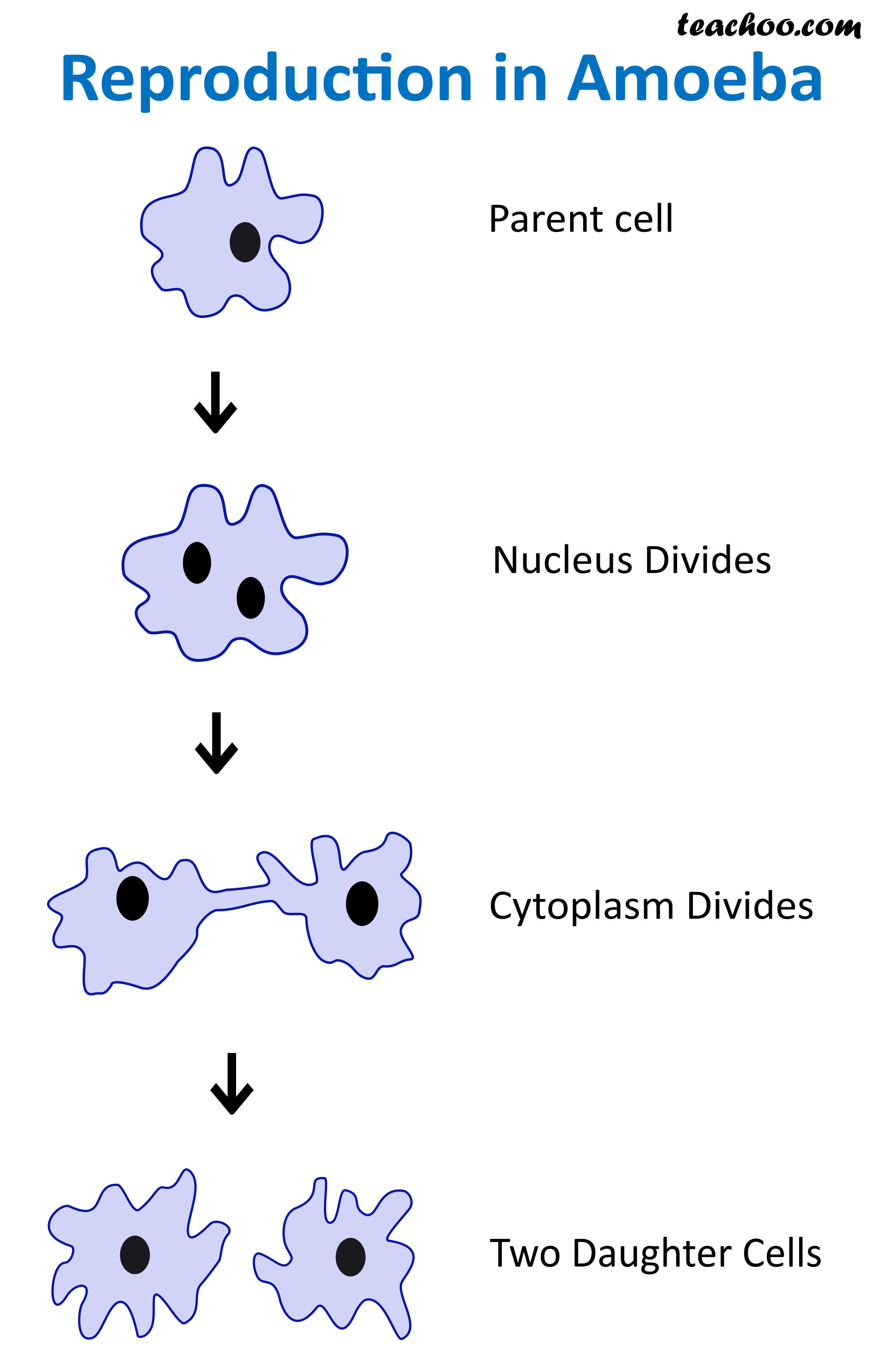

However, in multicellular organisms production of an offspring is a complex process with an elaborated involvement of many hormones. Origin of Fission Early 17th century: from Latin fissio(n-), from findere ‘to split’.In unicellular organisms, if the cell reproduces it gives rise to the new individual, but in multicellular organisms, the reproduction of a cell signifies regeneration and growth. The act or process of disintegration of an atomic nucleus into two or more smaller pieces called also nuclear fissionThe process may be spontaneous or induced by capture of neutrons or other smaller nuclei, and usually proceeds with evolution of energy. A process by which certain coral polyps, echinoderms, annelids, etc., spontaneously subdivide, each individual thus forming two or more new onesSee Strobilation. A method of asexual reproduction among the lowest (unicellular) organisms by means of a process of self-division, consisting of gradual division or cleavage of the into two parts, each of which then becomes a separate and independent organisms as when a cell in an animal or plant, or its germ, undergoes a spontaneous division, and the parts again subdivideSee Segmentation, and Cell division, under Division. A cleaving, splitting, or breaking up into parts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
